HORIBA contributes to the advancement and adoption of carbon resource recycling technology through its “measurement” technologies, covering processes, materials and gas monitoring at various stages. This includes analysis and quality control of recycled products, such as fuels and materials, as well as the analysis and evaluation of catalyst materials used in reaction processes.
Carbon resource recycling refers to the efficient use of carbon resources – such as CO2, biomass, and plastic waste – as synthetic fuels, chemicals, various materials, or energy, as well as the recycling of these resources. (Figure 1: Recycling and Utilization of Carbon Resources)
CO2 recycling includes synthetic fuel production, methane (CH4) production via methanation, and the generation of hydrogen and chemicals through artificial photosynthesis. Research, development and demonstrations are underway for synthetic fuels and synthetic methane produced using hydrogen derived from renewable energy sources and recovered CO2.
Biomass recycling can be used for power generation and fuels for mobility, in addition to its traditional use as feedstock and compost. In particular, fuels made from biomass are expected to serve as “drop-in fuels,” which can be blended with conventional fuels without requiring modifications to internal combustion engines.
Recycling of plastic waste involves material recycling, where plastic waste is reprocessed into raw materials for new plastics; chemical recycling, where it is gasified to produce hydrogen and synthesis gas for chemical and steel production; and thermal recovery, where plastic waste is used as fuel for different types of power generation and energy recovery.
To establish effective carbon resource recycling, the recycling of CO2, biomass, and plastic waste must be accelerated and expanded while reducing production costs and improving product quality. In particular, enhancing the performance, cost efficiency and durability of catalysts used in carbon resource recycling technologies is essential. Therefore, catalyst analysis and evaluation play a critical role from R&D to product manufacturing.
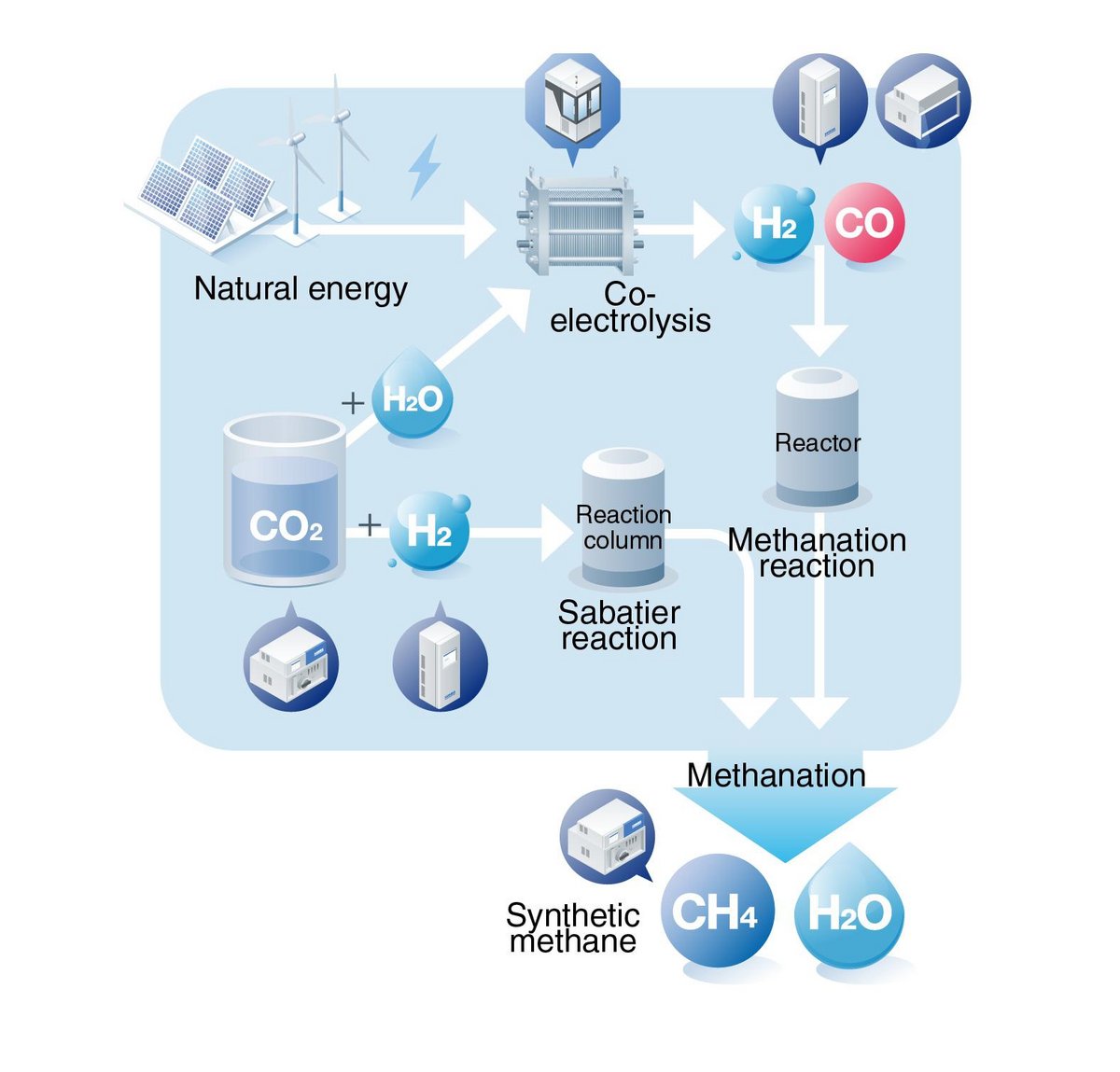
Typical CO2 recycling includes “synthetic fuel,” which is produced by reacting hydrogen produced by electrolyzing water with recovered CO2 using renewable energy, methane (CH4) production called “methanation,” production of chemicals using CO2 as raw material, and production of hydrogen and organic compounds by “artificial photosynthesis” combining sunlight, water, and CO2. photosynthesis, which combines sunlight, water, and CO2 to produce hydrogen and organic compounds.
For more information on CO2 capture technologies, please click here.
Syngas (hydrogen and CO) production technologies include “reverse shift reaction,” which converts CO2 to CO, “water electrolysis,” which breaks down water into hydrogen and oxygen by electrical force (electrolysis), and “co-electrolysis,” which simultaneously electrolyzes CO2 and water. In order to put these technologies to practical use and optimize them, various research and development efforts are underway to optimize the production ratio of H2 and CO, improve production energy efficiency, lower production costs including equipment, and improve durability. In “methanation,” where methane is produced by synthesizing water-electrolyzed hydrogen and CO2, practical application, and optimization of the methanation process using co-electrolysis, which has less heat loss due to waste heat compared to the Sabatier reaction, is also being promoted. For example, in the research and development of co-electrolysis using Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells (SOECs), it is important to evaluate SOECs under various environmental and test conditions in order to efficiently produce hydrogen and CO. In addition, to optimize the Sabatier reaction in methanation, it is essential to improve the yield of synthesis methane and the durability of the catalyst used.
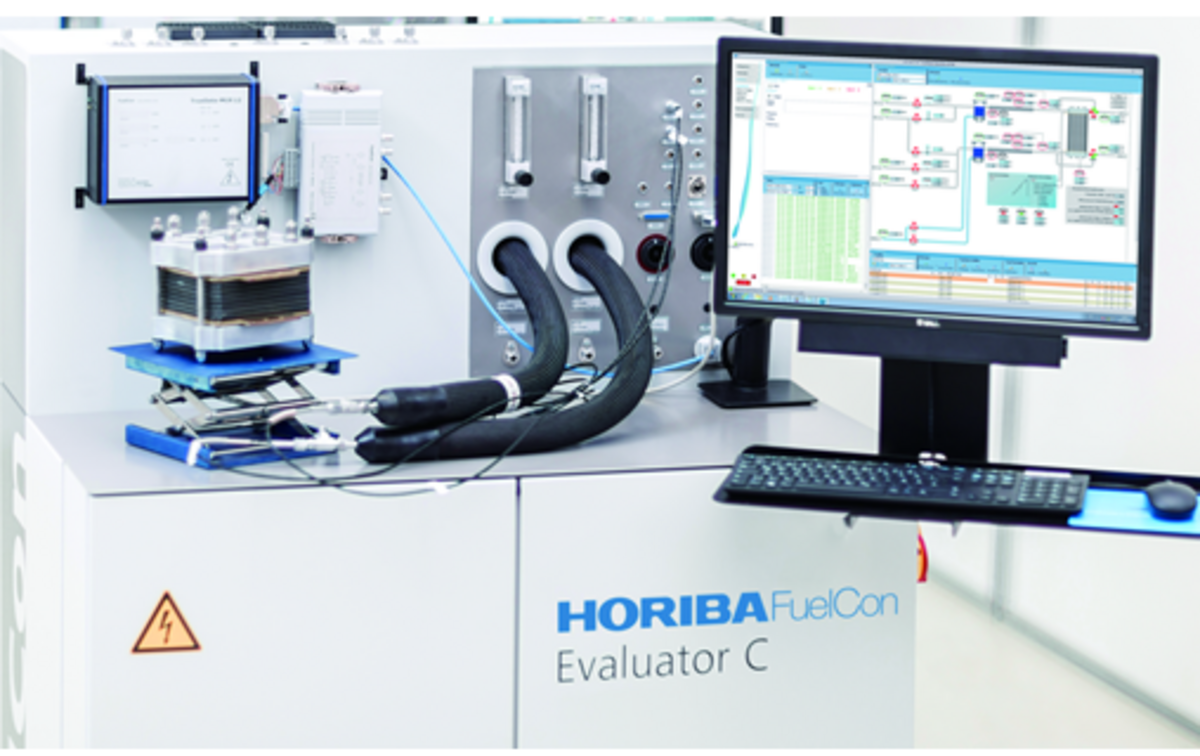
HORIBA contributes to solving customers' problems with a variety of analytical, measurement, testing and evaluation solutions from research and development to commercialization of synthesis gas (H2 and CO) production and methanation. Methanation requires measurement and monitoring of the concentrations of high concentrations of hydrogen and CO2 as raw materials and of the synthesized methane gas. The Evaluator EC / ES water electrolysis cell stack evaluation system flows various gases to evaluate the hydrogen production performance and durability of SOECs.
HORIBA Solutions >>
R&D Applications
For High-Speed Simultaneous Measurement of Multi-Component Gases: FTIR Method Exhaust Gas Analyzer FTX-ONE Series
For measurement of a wide variety of trace gas components generated: Multi-Component Gas Analyzer VA-5000 series
Manufacturing Applications
For measurement of major gas components:Explosion-proof process gas analyzer 51 series
In the process of producing liquid synthetic fuels from synthesis gas, synthesis crude oil is produced from synthesis gas by Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis, and the required type of liquid synthetic fuel (drop-in fuel) is produced by utilizing conventional refinery production technology and refining processes (up-grading) for the synthesis crude oil. HORIBA is contributing to the improvement of liquid synthetic fuel production technology by providing products, engineering and services based on its expertise in analytical and measurement technology in petroleum refining, which it has cultivated over many years in the United States.
HORIBA Solutions >>
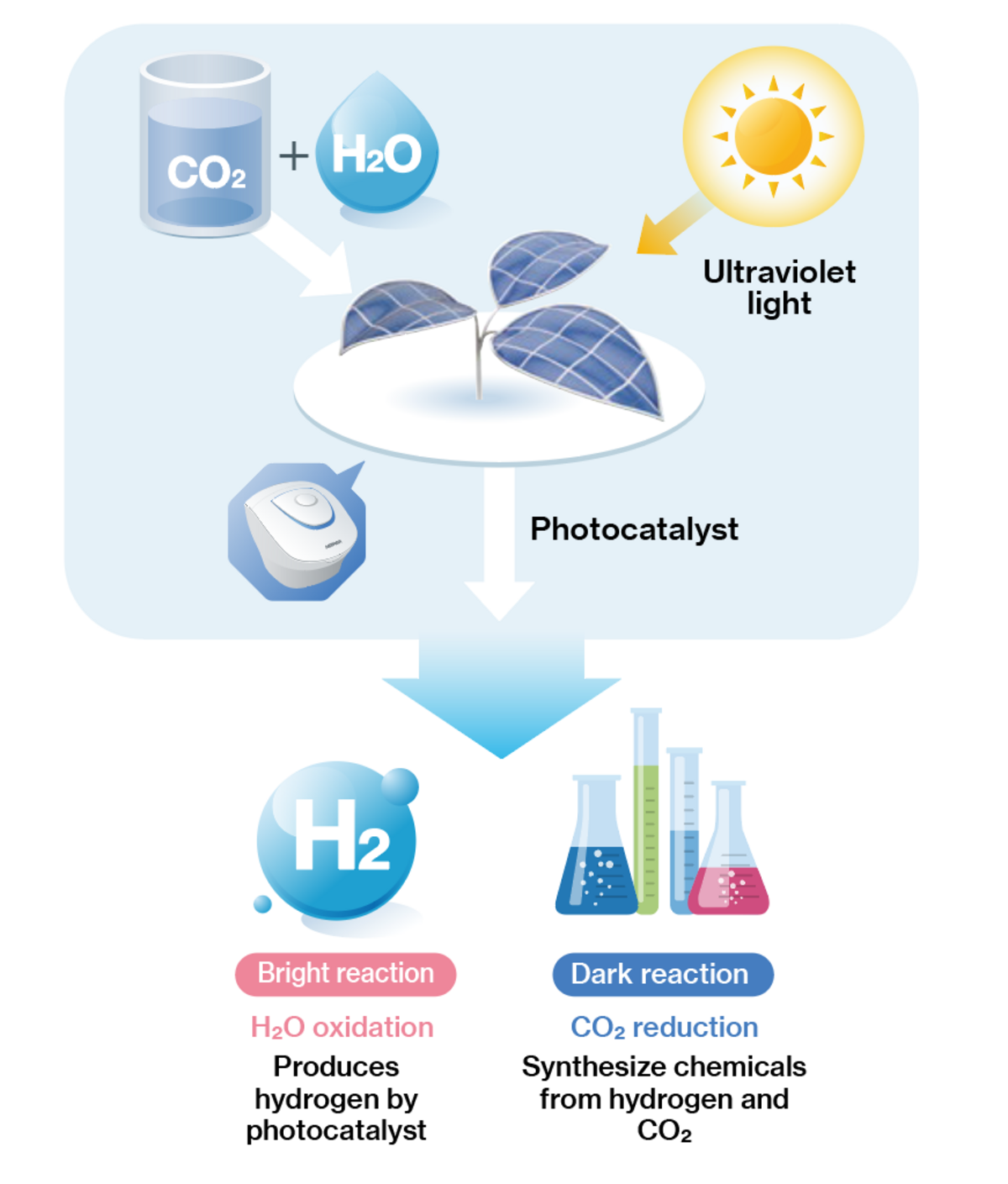
Artificial photosynthesis is a technology that uses solar energy to synthesize chemicals such as hydrogen and olefins from water and CO2. It is called “artificial photosynthesis” because it resembles the mechanism by which plants carry out photosynthesis from sunlight and CO2. Research and development of more efficient photocatalysts is underway with the aim of realizing a decarbonized society.
Sunlight contains light of a wide range of wavelengths, and it is important to utilize not only the short-wavelength region with high energy but also the long-wavelength region such as the near-infrared region. To evaluate the performance of complex catalysts used as photocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis, it is key to measure their excitation and fluorescence emission properties over a wide range of wavelengths.
HORIBA Solution >>
The fluorescence absorption spectrometer Duetta can evaluate luminescence properties in the near-infrared region, such as above 1,000 nm, and contributes to improving the reaction efficiency of catalytic materials.
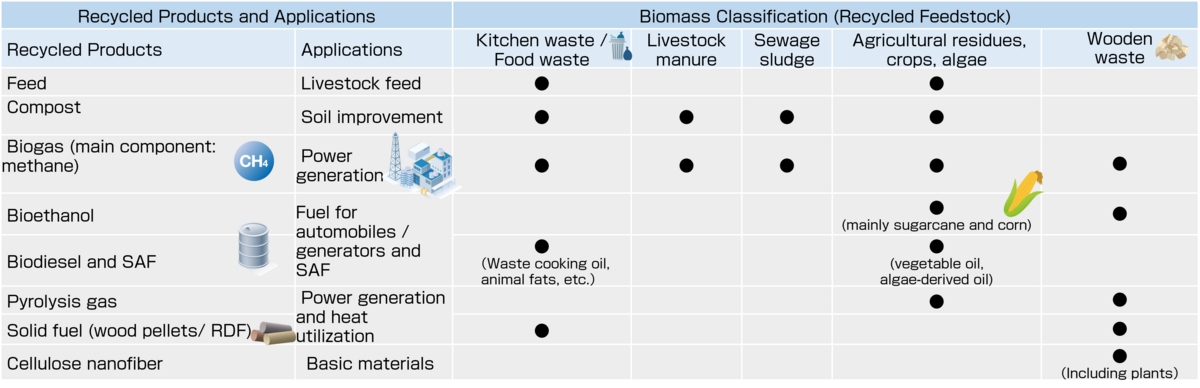
Biomass is an organic resource derived from living organisms, excluding fossil fuels. Biomass recycling makes it possible to effectively utilize biomass that was previously waste, such as forest thinning, livestock waste, and food waste, as a resource for a variety of uses (see table below).
Biomass can be burned in the same way as fossil fuels, and even when used for power generation and heat supply, it is attracting attention as a carbon-neutral resource that does not increase carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, unlike fossil resources.
Among the products produced from biomass recycling, bioethanol, biodiesel, and SAF (Sustainable Aviation Fuel) are used as mobility fuels for automobiles and aircraft. Biogas, pyrolysis gas, and waste-derived solid fuels derived from biomass are used as fuels in biomass power generation.
Fuels (biofuels) produced from biomass include bioethanol, biodiesel (FAME: Fatty Acid Methyl Ester), and hydrogenated vegetable oil (HVO: Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil), which are used in blends with conventional fuels, and the blending ratio with conventional fuels is expected to increase in the future. SAF (Sustainable Aviation Fuel), a biofuel for aviation fuel, can be classified into ATJ (Alcohol-to-Jet), HEFA (Hydro-processed Esters and Fatty Acids) FT (Fischer-Tropsch), etc., depending on the raw materials used and the manufacturing process, and the maximum blending ratio with conventional fuels is determined. In order to promote higher blending rates and substitution, it is necessary to establish and improve the supply chain to secure stable feedstock and supply, in addition to reducing the production cost, increasing calorific value, and reducing corrosiveness of biofuels.
The production lines and processes of conventional refineries (petroleum refineries) can also be utilized in the fuel production process using biomass. HORIBA provides products, engineering, and services based on its expertise in analytical and measurement technologies in petroleum refining, which it has cultivated over many years in the United States and contributes to the production of liquid fuels for mobility. When new fuels such as biofuels are actually used for mobility, it is important to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the performance and durability of the mobility itself.
HORIBA Solution >>
Measurement Solutions for Petroleum Refining Processes
Evaluation Systems for Vehicles and Engines
Biomass power generation can be achieved through direct combustion of biomass, pyrolysis of biomass at high temperatures to generate pyrolysis gas, and fermentation of biogas. HORIBA offers a broad lineup of analysis and measurement solutions, including equipment to improve power generation efficiency and to operate and manage exhaust gas treatment equipment, as well as continuous analysis equipment for special gases such as siloxane contained in biogas, thereby helping to solve issues related to biomass power generation.
Biomass Power Generation
HORIBA Solution >>
More detailed measurement solutions for biomass and biogas power generation
When energy is recovered as heat by burning non-recyclable biomass materials at waste disposal sites or waste incineration plants, the same issues that arise in power generation using plastic waste as fuel in thermal recovery may arise. For more information, please click here: Analysis and Measurement Solutions for Waste Power Generation
Cellulose nanofiber (CNF), which is made from wood and plant-derived biomass, is a new material that is one-fifth as light as steel but five times stronger. It is expected to be utilized in various foundational materials. For quality control and utilization of CNF, it is necessary to grasp the size of the fibers and the dispersion state in liquids (gels) at high speed and high resolution. HORIBA proposes a particle evaluation system that enables the evaluation of material properties at the nano-level.
HORIBA Solutions >>
For Particle Size Distribution Measurement of CNF: Centrifugal Nano Particle Analyzer Partica CENTRIFUGE
For structural evaluation of CNF gel materials: nanoPartica SZ-100V2
The active reuse (recycling) of plastic waste as a resource is expected to reduce the use of new fossil resources and CO2 emissions, thereby contributing to the recycling of carbon resources.
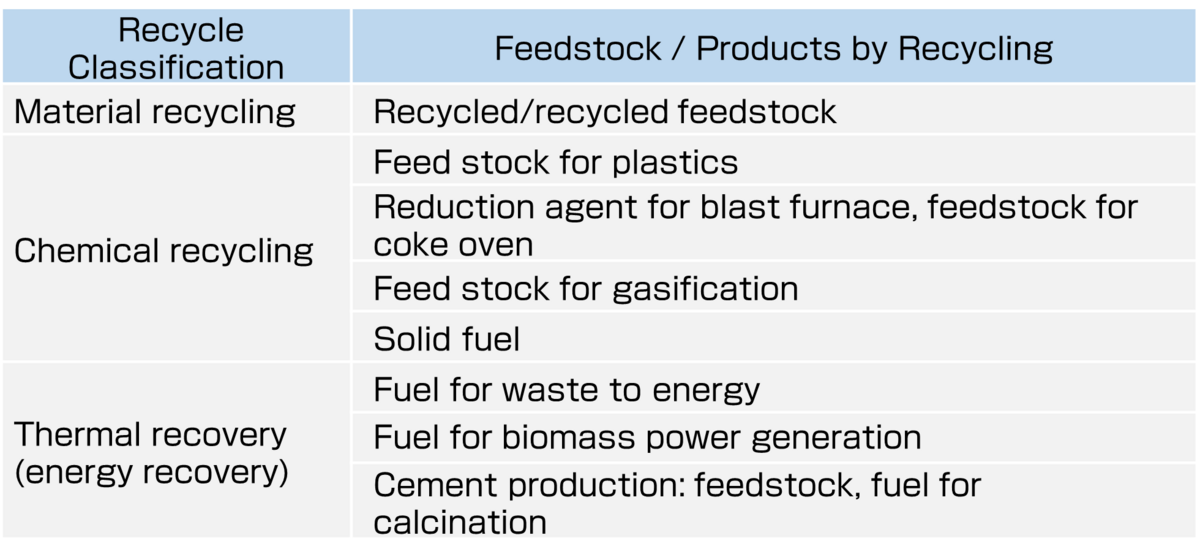
Effective use of recycled plastic is achieved through material recycling, which recycles plastic waste into raw materials for plastic products; chemical recycling, which produces raw materials for chemicals and steelmaking and hydrogen and synthetic fuels; and thermal recovery, which burns plastic waste unsuitable for the material/chemical cycle and recovers it as energy (see table below).
In material recycling, waste plastics are used as raw materials to make new products. In the process of waste plastic sorting and reprocessing, it is important to determine the type of plastic used as raw material.
HORIBA provides solutions to determine the type of plastic by using new analysis and measurement methods.
HORIBA Solution >>
Non-contact automatic plastic identification: Hyperspectral camera and imaging systems
Research and development are also underway to link chemical recycling and next-generation alternative energy production, such as the production of ammonia (NH3) from the produced hydrogen. For safe and highly efficient gasification, continuous measurement of generated gas, added gas, impurity gas, exhaust gas, etc. at gasifiers and other process facilities is necessary.
HORIBA Solution >>
HORIBA provides the necessary gas analyzers that are indispensable for monitoring the gasification of plastic waste, optimized for the customer's production facilities and operating environment.
For measuring gas concentration of each component in pyrolysis gas: Multi-Component Gas Analyzer VA-5000 series, Stack Gas Analysis System ENDA-5000 series
For measurement of O2 concentration to improve combustion efficiency or to confirm incomplete combustion: Zirconia Oxygen Analyzer NZ-3000
For measuring gas concentration for monitoring denitration/desulfurization and flue gas monitoring:Stack Gas Analysis System ENDA-5000 series
For measuring various gas concentrations in explosion-proof area:Explosion-proof process gas analyzer 51 series
The use of plastic waste as a reductant for blast furnaces and raw material for coke ovens reduces the number of resources needed for steelmaking. Continuous gas measurement of gases generated in blast furnaces and coke ovens helps to understand the impact of using plastic waste.
HORIBA Solutions >>
Solutions for the steel industry are summarized here. Please take a look.
Of the three types of recycling, thermal recovery is currently the most utilized. Solid fuel (RPF) made from plastic waste and recovered paper and plastic waste can be recovered as energy by using them as fuel for power generation at waste incineration plants and industrial waste treatment plants. To improve the energy recovery rate through thermal recovery, it is necessary to optimize the operating conditions of each facility, such as the incineration facility, gasification facility, and power generation facility. HORIBA will continue to develop solutions for thermal recovery with new measurement methods and analyzers.
RPF (Refuse Paper and Plastic Fuel) is a solid fuel made mainly from wastepaper and plastic, which is also used as fuel for power generation and gasification of plastic waste.
Screening analysis of chlorine content in RPF
RPF may contain chlorine (Cl), which is one of the causes of incinerator degradation. before using RPF as fuel for incinerators, chlorine content can be checked and removed to prevent incinerator degradation.
HORIBA Solution >>
For screening analysis of chlorine content in RPF: Desktop X-ray Fluorescence Analyzer MESA-50
Industrial waste power generation and waste incineration power generation require different treatment processes than general thermal power generation, such as the treatment of hydrogen chloride (HCl), which is one of the various issues generated by plastic waste combustion. In addition, since power generation efficiency is not very high compared to general thermal power generation, the introduction of waste gasification technology to improve power generation efficiency is also in progress. HORIBA offers a wide lineup of analyzers, including continuous gas analyzers, which are necessary for improving power generation efficiency and for operating and managing waste gas treatment equipment, thereby helping to solve problems in waste power generation.
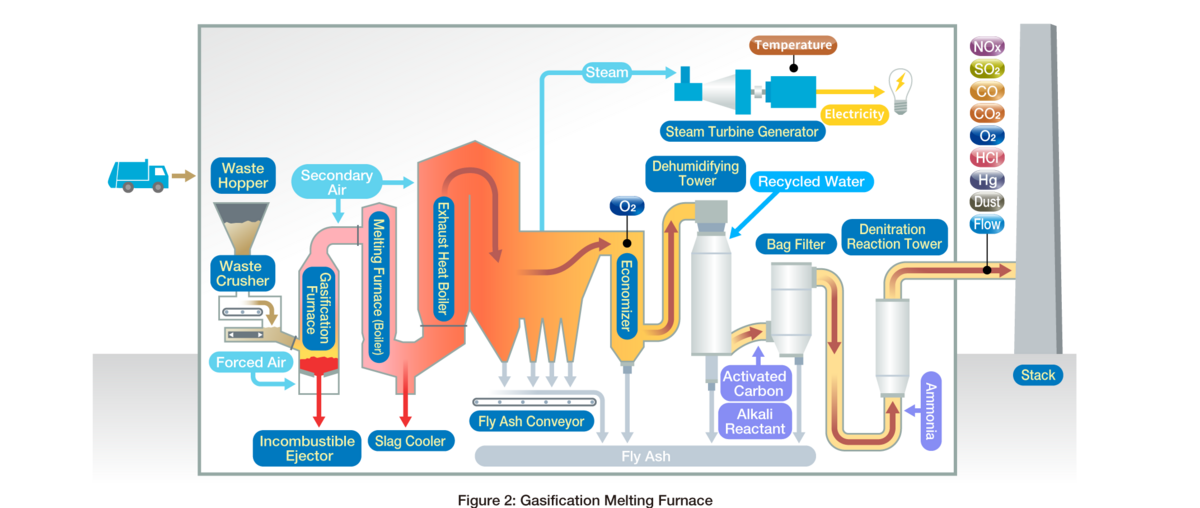
Example of Waste to Energy Gasification Plant
HORIBA Solution >>
Solutions for waste power generation are summarized here. Please take a look.
In the calcination process of cement production, plastic waste and biomass are used as fuel for temporary combustion furnaces that generate heat for pre-heaters and for rotary kilns. Some plants also combine methanation facilities that use CO2 emitted from the calcination process as a raw material. HORIBA offers a wide lineup of analyzers, including continuous gas analyzers, which are necessary for improving productivity and operating and managing waste gas treatment equipment, thereby helping to solve problems in cement production.
To establish carbon resource recycling, it is necessary to accelerate and expand CO2 recycling, biomass recycling, and plastic waste recycling. Common issues in carbon resource recycling include reducing manufacturing costs and improving the quality of the final product. In particular, improving the performance, cost, and durability of catalysts used in various manufacturing processes is directly related to solving these issues. Thus, carbon resource recycling and catalysts are closely related, and catalysts are evaluated and improved in each phase of catalyst R&D, demonstration of each process, social implementation, and product manufacturing at plants and other facilities. Specifically, it is important to ensure the quality of carbon resources, stable process operation, and elimination of impurities to prevent performance degradation and deterioration due to catalyst carbonization and poisoning.
HORIBA supports the R&D of catalysts for carbon recycling to the manufacturing of final products using catalyst-based processes with a variety of analytical, measurement, testing and evaluation solutions.
We have a long-standing commitment to analysis and evaluation of advanced materials. Your sample is measured by a highly trained member of our Application Centers and presented as a formal report complete with method, observations, results, and data interpretation assistance.
In addition to consultation on the selection of analytical instruments, we also provide analytical technologies through services such as contract analysis and joint research with customers and academia, utilizing our know-how and skills as an analytical instrument manufacturer.
Do you have any questions or requests? Use this form to contact our specialists.