
The behavior of an abrasive material is influenced by the hardness, size, and shape of the particles. A harder particle will be more aggressive in altering the surface of the work piece. Larger particles generate higher impact force removing the material surface quicker and producing a heavier texture. Particle shape also plays a role. Particles with points and edges remove surface material on impact, while round particles without cutting edges are used to pound or “peen” a surface.
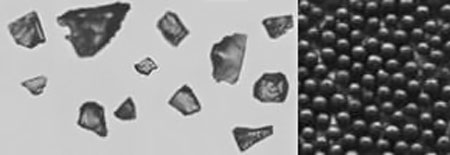
Sharp Edge Abrasives (left) and Round Abrasive (right)
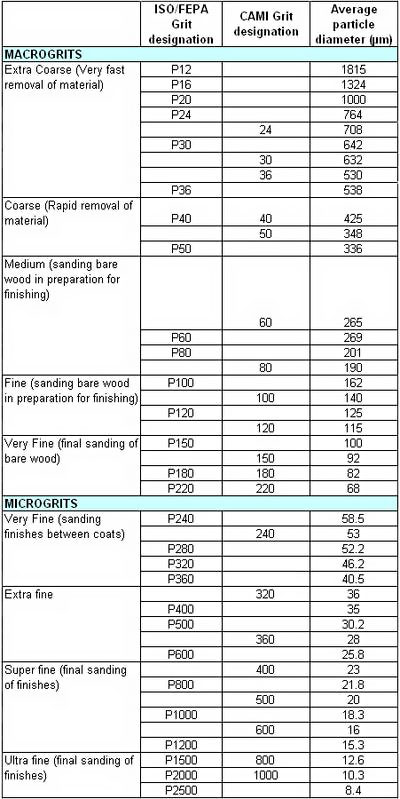
Particle size analysis of abrasives had traditionally been performed using sieves and sedimentation. This led to a split between macrogrits based on screen sizes (4 to 220) and microgrits based on sedimentation (240 and below). Various standards exist for classifying the size range of abrasive materials. The table below compares Coated Abrasive Manufacturers Institute (CAMI) and Federation of European Producers of Abrasives (FEPA) "P" designations with the average grit size in microns (µm).
The laser diffraction technique is capable of covering almost all of the abrasive size ranges and is quicker and easier than either sieves or sedimentation. For this reason laser diffraction is becoming more popular as a technique. Results from the LA-960V2 laser diffraction analyzer for diamond and silicon carbide abrasives are shown below.
Diamond abrasives using laser diffraction.![]()
Silicon carbide using laser diffraction.
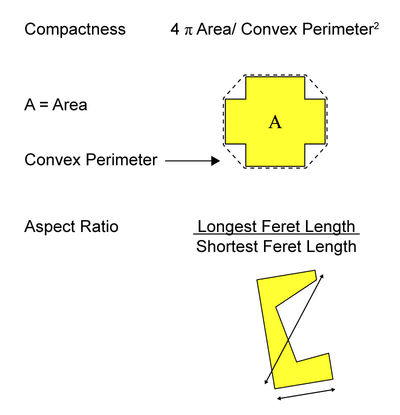
Automated image analysis provides not only particle size distribution, but also particle shape information. The additional morphology information is important for abrasives because the presence of sharp edges typically enhances abrasive performance.
Laser Scattering Particle Size Distribution Analyzer
Masz pytania lub prośby? Skorzystaj z tego formularza, aby skontaktować się z naszymi specjalistami.