Ammonia is attracting attention as a next-generation clean fuel, but its effective use requires optimizing its synthesis and decomposition processes. A key factor that greatly impacts this efficiency is the catalyst used for ammonia synthesis and decomposition.
To evaluate catalyst performance, real-time analysis of ammonia concentration is essential. However, traditional methods have been limited to intermittent techniques, such as gas chromatography quantification or capturing ammonia with hazardous sulfuric acid and measuring its concentration through conductivity changes.
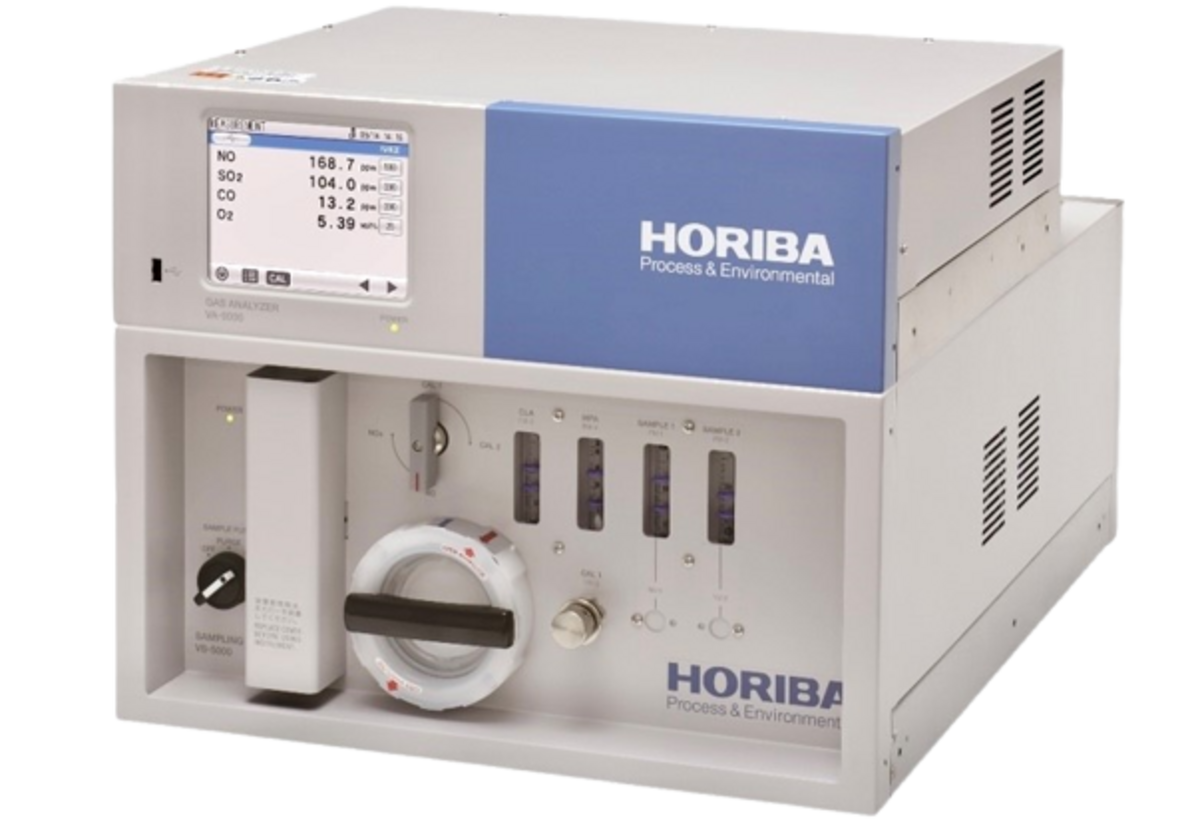
Utilizes non-dispersive infrared (NDIR) absorption technology, enabling long-term stable and continuous NH3 measurement.
Available with maximum 0-100 vol% and minimum 0-100 ppm measurement ranges (only for dry gas).
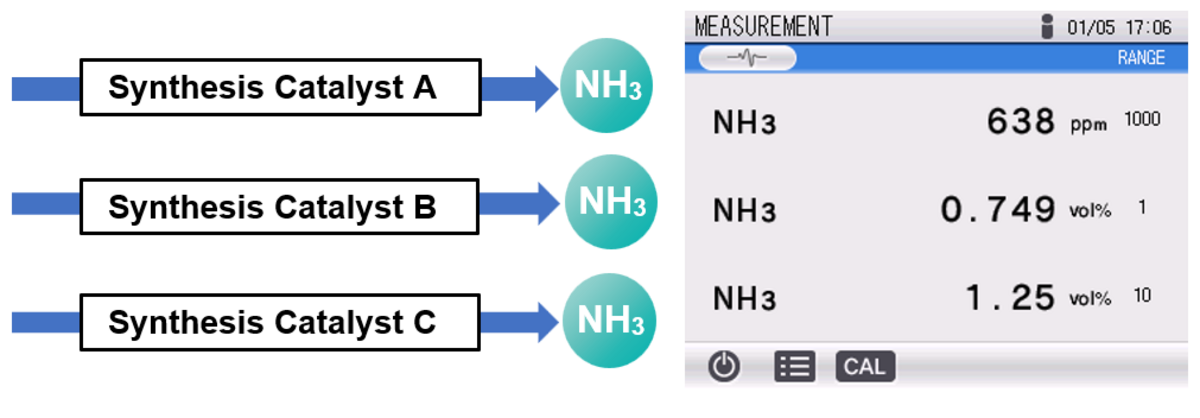
Supports up to three NH3 detectors for parallel installation and simultaneous catalytic reaction monitoring.
Figure 2: VA-5111 model with three NH3 detectors installed
Multi-Component Gas Analyzer VA-5000 Series
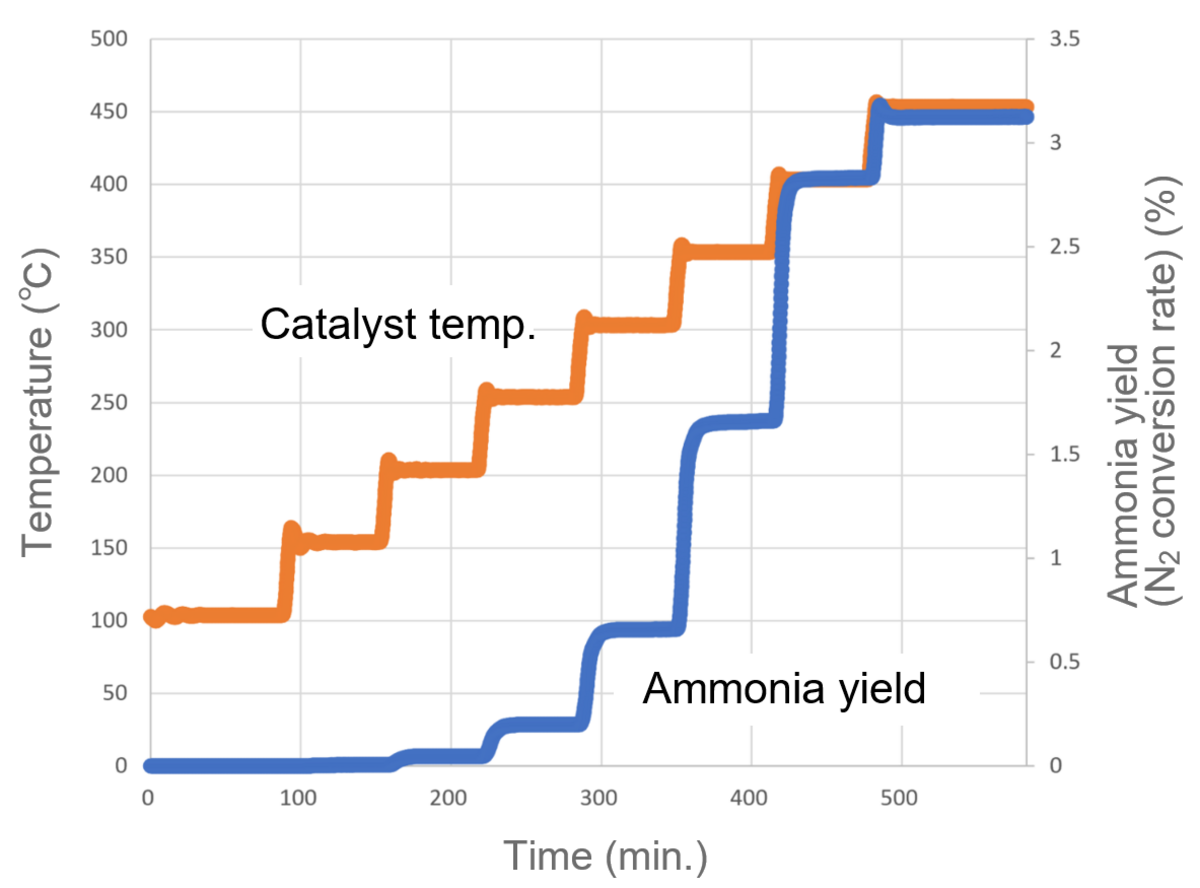
Figure 1: Ammonia Synthesis Results using Co/Ba/MgO Catalyst
Data provided by Nagoya University, Dept of Chemical Systems Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, Nagaoka Laboratory
Before implementing the system, conductivity had to be measured manually while adjusting sulfuric acid concentrations to match ammonia levels, making the process both complex and hazardous. With the VA-5000, measurements are now automated and safe, allowing for a larger number of experiments.
Katsutoshi Nagaoka, Dr. Eng. Professor,
Nagoya University, Department of Chemical Systems Engineering,
Graduate School of Engineering, Institute of Innovation for Future Society
Multi-Component Gas Analyzer
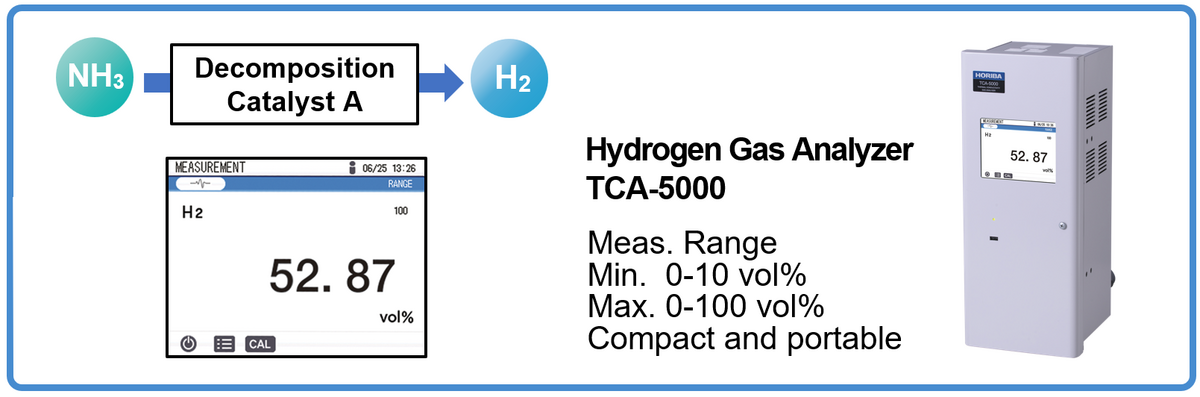
Hydrogen Gas Analyzer
Máte nějaké dotazy nebo požadavky? Pomocí tohoto formuláře kontaktujte naše specialisty.